European bisphenol A ban - a step towards a healthier environment
It is found in many everyday products - from plastic bottles to food packaging to electronic items. Bisphenol A (BPA), as it is referred to, is a chemical that has been widely used for many years in the production of plastics and epoxy resins.
It is found in many everyday products - from plastic bottles to food packaging to electronic items. Bisphenol A (BPA), as it is referred to, is a chemical that has been widely used for many years in the production of plastics and epoxy resins.
Over time, more and more studies began to show that BPA could have a negative impact on our health and the environment. In response to growing concerns, bisphenol A was banned in European Union countries. Manufacturers who used it will have 18 months to replace it with another compound.
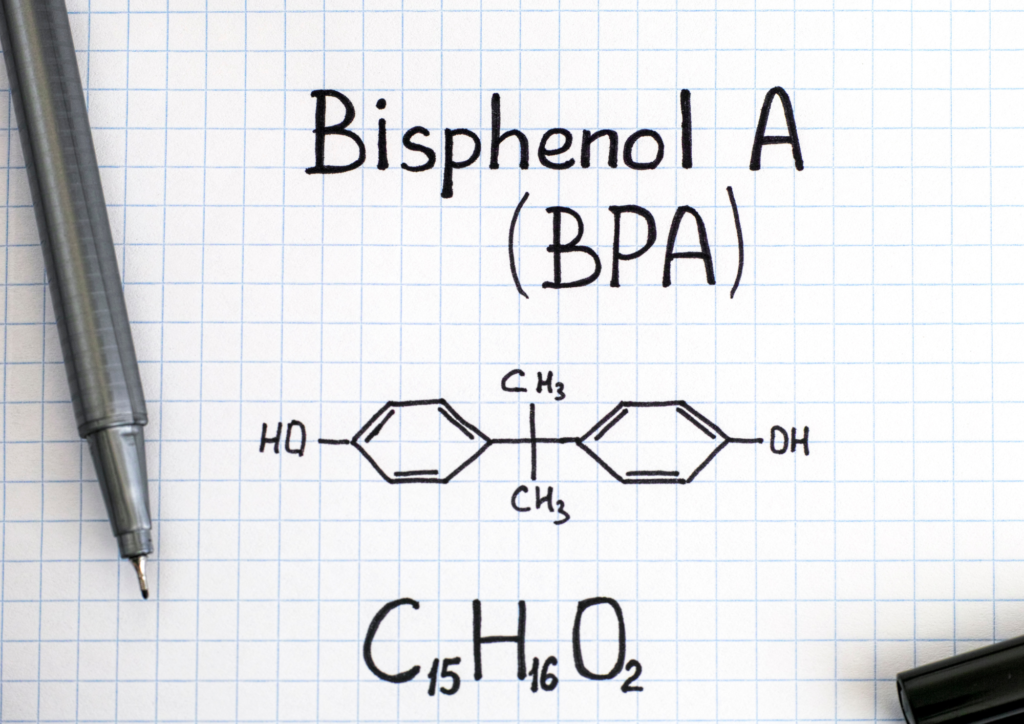
What is bisphenol A (BPA) and why is it dangerous?
Bisphenol A is an organic chemical compound mainly used in the production of plastics - especially polycarbonate and epoxy resins. We can find it in many everyday objects. Examples include bottles, cups, food containers and also in the protective coating inside food cans. BPA can penetrate food or beverages and then enter the human body, raising serious health concerns.
Studies have shown that BPA can disrupt the endocrine system and even cause changes in the structure of DNA. The substance is called 'endocrinally active' because it can interfere with the natural process of hormone secretion in human and animal bodies. Overexposure to BPA can therefore lead to health problems. We are talking about problems such as fetal and child development disorders, heart disease, obesity, diabetes and even fertility problems.
What benefits will the BPA ban bring?
- Protection of human health - The ban on BPA in food products helps to reduce the risk of exposure to chemicals that can affect human development and health.
- Sustainability and environmental protection - BPA is a substance that is difficult to break down in the environment. This means that once it has been released into nature, it can persist in the soil, water or air for a long time.
- Innovation and alternatives - The ban on BPA creates space for the development of new, safer technologies and materials. The industry will need to focus on creating alternative plastics that do not have negative health and environmental impacts. This could contribute to the development of more sustainable solutions in plastics and packaging production.

What can we do to protect ourselves and the environment?
While Europe's ban on BPA is a huge step forward, each of us can take action today to reduce our exposure to the chemical and look after our health and the environment:
- Choose BPA-free products - Pay attention to labels and choose products that are labelled 'BPA free'. Many companies now offer alternatives such as BPA-free glass, steel or plastic bottles. Whenever possible, choose fresh food over packaged food.
- Avoid plastic in contact with food - try not to use plastic to store food. Most importantly, don't heat food in containers containing BPA, as high temperatures can increase its release. Choose glass or ceramic containers, which are safer and more environmentally friendly.
- Recycling and proper separation of waste - Plastic packaging, including that containing BPA, should be properly segregated and recycled to reduce its impact on the environment.
- Environmental education - The more we know about the risks associated with chemicals, the better decisions we make.
The European Union's ban on bisphenol A (BPA) is an important step towards protecting human health and the environment. With initiatives like this, we reduce exposure to chemicals that can have serious health consequences. However, each of these decisions starts with us - with our informed approach to shopping and our daily choices.



